Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
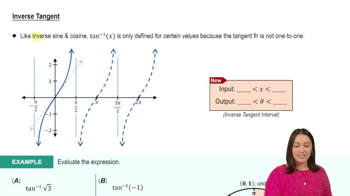
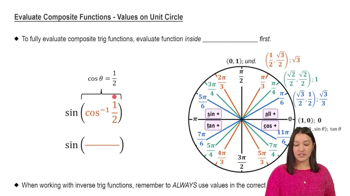
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
0. Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
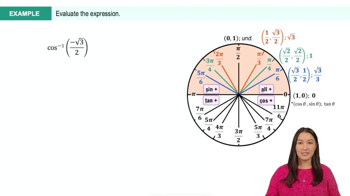
Problem 3.10.80a
Textbook Question
Tracking a dive A biologist standing at the bottom of an 80-foot vertical cliff watches a peregrine falcon dive from the top of the cliff at a 45° angle from the horizontal (see figure). <IMAGE>
a. Express the angle of elevation θ from the biologist to the falcon as a function of the height h of the bird above the ground. (Hint: The vertical distance between the top of the cliff and the falcon is 80−h.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the right triangle formed by the cliff, the horizontal distance from the biologist to the falcon, and the line of sight from the biologist to the falcon. The height of the triangle is the vertical distance from the biologist to the falcon, which is 80 - h.
Recognize that the angle of elevation θ is the angle between the horizontal line from the biologist and the line of sight to the falcon.
Use the tangent function, which relates the angle of elevation θ to the opposite side (80 - h) and the adjacent side (horizontal distance x) of the right triangle: tan(θ) = (80 - h) / x.
Since the falcon dives at a 45° angle from the horizontal, the horizontal distance x is equal to the vertical distance from the top of the cliff to the falcon, which is also 80 - h.
Substitute x = 80 - h into the tangent function: tan(θ) = (80 - h) / (80 - h) = 1. Therefore, θ = arctan(1), which simplifies to θ = 45°.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. In this context, the angle of elevation θ can be expressed using the tangent function, which is the ratio of the opposite side (the height of the falcon above the ground) to the adjacent side (the horizontal distance from the biologist to the falcon). Understanding these functions is essential for solving problems involving angles and distances.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Angle of Elevation
The angle of elevation is the angle formed by the horizontal line and the line of sight to an object above that line. In this scenario, the biologist observes the falcon diving, and the angle of elevation θ can be calculated based on the height of the falcon above the ground. This concept is crucial for determining how the height of the falcon changes the angle from the observer's perspective.
Recommended video:
Trig Values in Quadrants II, III, & IV Example 2
Vertical and Horizontal Distances
In this problem, the vertical distance is the height of the falcon above the ground, while the horizontal distance is the distance from the biologist to the point directly below the falcon. The relationship between these distances is key to forming a right triangle, which allows the use of trigonometric functions to express the angle of elevation as a function of the falcon's height. Understanding these distances is vital for applying trigonometry effectively.
Recommended video:

Derivatives Applied To Velocity Example 1
Related Videos
Related Practice