Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 52m
- Introduction to Functions16m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms34m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 2h 22m
4. Applications of Derivatives
Differentials
Problem 19
Textbook Question
Lapse rates in the atmosphere Refer to Example 2. Concurrent measurements indicate that at an elevation of 6.1 km, the temperature is -10.3° C and at an elevation of 3.2km , the temperature is 8.0°C . Based on the Mean Value Theorem, can you conclude that the lapse rate exceeds the threshold value of 7°C/ km at some intermediate elevation? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
First, understand the concept of the Mean Value Theorem (MVT). The MVT states that for a function that is continuous on a closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), there exists at least one point c in (a, b) such that the derivative at c is equal to the average rate of change over [a, b].
Identify the function and interval in this problem. The function here is the temperature T as a function of elevation h, and the interval is [3.2, 6.1] km.
Calculate the average rate of change of temperature over the interval [3.2, 6.1] km. This is done by finding the difference in temperature divided by the difference in elevation: \( \frac{T(6.1) - T(3.2)}{6.1 - 3.2} \).
Substitute the given temperatures into the formula: \( \frac{-10.3 - 8.0}{6.1 - 3.2} \). This will give you the average rate of change of temperature with respect to elevation over the interval.
Compare the calculated average rate of change to the threshold value of 7°C/km. If the average rate of change exceeds 7°C/km, then by the Mean Value Theorem, there exists at least one elevation between 3.2 km and 6.1 km where the lapse rate exceeds 7°C/km.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mean Value Theorem
The Mean Value Theorem states that if a function is continuous on a closed interval and differentiable on the open interval, there exists at least one point where the derivative of the function equals the average rate of change over that interval. In the context of lapse rates, it implies that there is at least one elevation where the instantaneous rate of temperature change matches the average rate calculated between two points.
Recommended video:

Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 1
Lapse Rate
Lapse rate refers to the rate at which temperature decreases with an increase in altitude in the atmosphere. It is typically expressed in degrees Celsius per kilometer (°C/km). Understanding lapse rates is crucial for analyzing atmospheric conditions, as they can indicate stability or instability in the atmosphere, affecting weather patterns and phenomena.
Recommended video:
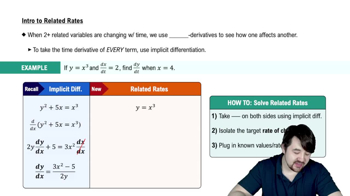
Intro To Related Rates
Average Rate of Change
The average rate of change of a function over an interval is calculated by taking the difference in the function's values at the endpoints of the interval and dividing it by the difference in the input values. In this case, it helps determine the overall change in temperature between two elevations, which can then be compared to the threshold lapse rate to assess if the instantaneous lapse rate exceeds that value at some point in between.
Recommended video:

Average Value of a Function