Why does altruism seem paradoxical? a. Sometimes altruistic behavior is actually selfish. b. Altruism does not actually help others. c. Alleles that cause an organism to behave altruistically should be selected against since these alleles should lower the organism's fitness. d. Animals behave altruistically to help the species, but sometimes their behavior harms the species.
Propose an evolutionary hypothesis to explain the observation that some bird populations do not migrate if people supply food for them in feeders.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Natural Selection

Behavioral Adaptation

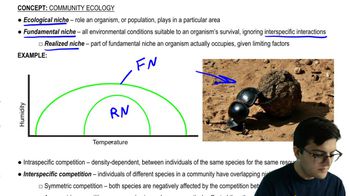
Ecological Niche
Is it true that all organisms forage optimally? Why or why not?
The male cuttlefish in the chapter-opening photo can rapidly change their skin colors (under nerve control) to flash warning patterns to rivals. Predict the proximate and ultimate causes of this behavior.
Hamilton's rule states that an altruistic allele could spread in a population if Br > C, where B represents the fitness benefit to the recipient, r is the coefficient of relatedness between altruist and recipient, and C represents the fitness cost to the altruist. If r=0.5 between the altruist and the recipient, what would the ratio of costs to benefits have to be for the altruistic allele to spread? a. C/B > 0.5 b. C/B > 0 c. C/B < 0.5 d. C/B < 0
Evolutionary biologist Hopi Hoekstra and colleagues have hypothesized that the burrow-digging behavior of mice (and the resulting shape of their underground burrows) is heritable—innate and not learned. Design an experiment to test this hypothesis.
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them. Whales communicate with one another using sound. What is one benefit and one cost to whales of using sound to communicate underwater?
