Propose a hypothesis to explain how self-reactive B cells are identified and eliminated during maturation.
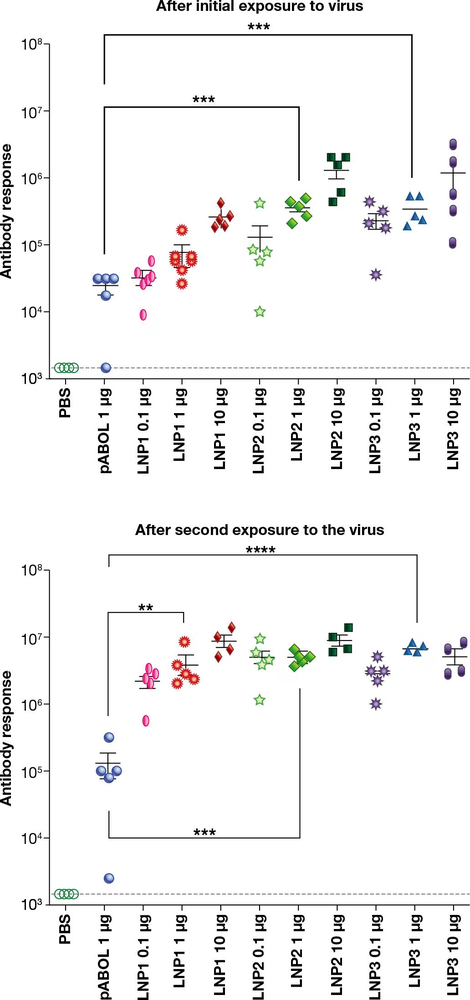
Dr. Anna Blakney, bioengineer and RNA scientist, as part of a multidisciplinary team, compared the immune response from different formulations for delivering self-amplifying RNA encoding a viral antigen to cells. The team tested a cationic polymer (pABOL) and three lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Five female mice per treatment group were intramuscularly immunized with increasing microgram (µg) doses of self-amplifying RNA formulated with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline control), pABOL, LNP1, LNP2, or LNP3. Blood was collected to measure the antibody responses at four (A) and six weeks (B). The colored dots represent individual animals, and the asterisks indicate 𝑃 values (for help interpreting the graph, see BioSkills 2 and 3). What conclusion is supported by the results shown in the dot plot graphs below?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Self-Amplifying RNA

Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)

Antibody Response Measurement
What are two main criteria required for an RNA vaccine to be effective at protecting a vaccinated individual from a viral infection?
Self-amplifying RNA vaccines currently being developed are typically derived from alphaviruses—Class IV, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses. Explain why an alphavirus is a good choice.
Before the RNA is translated into a viral antigen that can induce an antibody response, what other cellular response could be triggered by a self-amplifying RNA vaccine?
Lipid nanoparticle formulations of self-amplifying RNA contain lipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol (for review, see Ch. 7, Section 7.5). By which process do they enter cells?
a. beating cilia
b. phagocytosis
c. receptor-mediated endocytosis
d. macropinocytosis
Compared with non-replicating mRNA vaccines, a smaller dose of self-amplifying RNA is needed to induce a protective immune response. What are possible advantages of being able to use a smaller dose of a vaccine during a pandemic?
