What term describes the mode of asexual reproduction in which offspring develop from unfertilized eggs?
a. Parthenogenesis
b. Budding
c. Regeneration
d. Fission

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What term describes the mode of asexual reproduction in which offspring develop from unfertilized eggs?
a. Parthenogenesis
b. Budding
c. Regeneration
d. Fission
In sperm competition, what is 'second-male advantage'?
a. The observation that when females mate with two males, each male fertilizes the same number of eggs
b. The observation that when females mate with two males, the second male fertilizes most of the eggs
c. The observation that females routinely mate with at least two males before laying eggs or becoming pregnant
d. The observation that accessory fluids prevent matings by second males—for example, by forming copulatory plugs
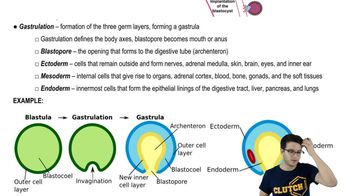
Which of the following statements regarding animal development is/are correct? Select True or False for each statement.
T/FThe neural tube forms after organogenesis is complete
T/FThe blastocyst is formed during cleavage
T/FDuring cleavage, the zygote divides rapidly without growth, forming a mass of cells
T/FAnimals have two germ layers
Summarize the experimental evidence that Daphnia require three cues to trigger sexual reproduction. Discuss what these cues indicate about the environment.
Many frogs and mice are similar in size, yet a frog egg is vastly larger than a mouse egg. Propose a plausible explanation for this difference in the egg size.
How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis in humans differ with respect to numbers of cells produced, gamete size, and timing of the second meiotic division?