What is apoptosis? a. an experimental technique used to kill specific cells b. programmed cell death that is required for normal development c. a pathological condition observed only in damaged or diseased organisms d. a developmental mechanism unique to the roundworm C. elegans
In adult animals, are a source of undifferentiated cells that can divide to produce cells that can specialize.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Stem Cells
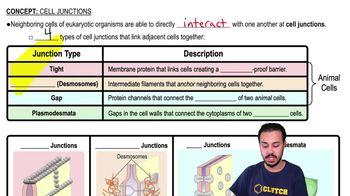
Cell Differentiation

Tissue Regeneration

What term describes the mode of asexual reproduction in which offspring develop from unfertilized eggs? a. parthenogenesis b. budding c. regeneration d. fission
In sperm competition, what is 'second-male advantage'? a. the observation that when females mate with two males, each male fertilizes the same number of eggs b. the observation that when females mate with two males, the second male fertilizes most of the eggs c. the observation that females routinely mate with at least two males before laying eggs or becoming pregnant d. the observation that accessory fluids prevent matings by second males—for example, by forming copulatory plugs
Which of the following statements regarding animal development is/are correct? Select True or False for each statement. T/F The neural tube forms after organogenesis is complete T/F The blastocyst is formed during cleavage T/F During cleavage, the zygote divides rapidly without growth, forming a mass of cells T/F Animals have two germ layers
True or false: The corpus luteum is retained upon implantation due to the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
