Which of these statements about myelination in neurons is/are correct? Select True or False for each statement. T/F It speeds propagation by increasing the density of voltage-gated channels all along the axon. T/F Multiple sclerosis is characterized by disrupted myelination of certain neurons in the central nervous system. T/F It speeds propagation by preventing cations from leaking out across the membrane as they spread down the axon. T/F It is more commonly observed in vertebrates than in invertebrates.
Ch. 43 - Animal Nervous Systems
Chapter 42, Problem 1
Which ion most readily leaks across a neuron's membrane, helping to establish the resting potential?

Verified Solution
Video duration:
58sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
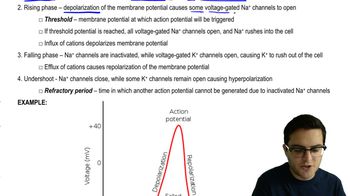
Resting Potential
Resting potential refers to the electrical charge difference across a neuron's membrane when it is not actively transmitting a signal. This potential is typically around -70 mV and is maintained by the distribution of ions, particularly sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), across the membrane. The resting potential is crucial for the generation of action potentials, which are necessary for neuronal communication.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Action Potential
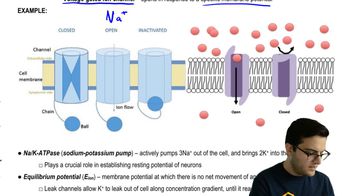
Ion Channels
Ion channels are protein structures embedded in the cell membrane that allow specific ions to pass in and out of the neuron. These channels can be voltage-gated or leak channels, with leak channels being responsible for the passive movement of ions, such as potassium (K+), which predominantly leaks out of the neuron, contributing to the resting potential. The selective permeability of these channels is vital for maintaining the resting state of the neuron.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Ion Channels and Pumps
Potassium Ions (K+)
Potassium ions (K+) are the primary ions that leak across the neuron's membrane, significantly influencing the resting potential. Due to a higher concentration of K+ inside the neuron compared to the outside, K+ ions tend to diffuse out through leak channels. This efflux of K+ contributes to the negative charge inside the neuron, establishing the resting potential and preparing the neuron for potential action potentials.
Recommended video:
Guided course
r/K Selection
Related Practice
Textbook Question
710
views
Textbook Question
In a neuron, what creates the electrochemical gradient favoring the outflow of K+ when the cell is at rest? a. Na+/K+-ATPase b. voltage-gated K+ channels c. voltage-gated Na+ channels d. ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels
560
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following brain regions is responsible for formation of new memories? a. brainstem b. cerebellum c. frontal lobe d. hippocampus
717
views
