Which ion most readily leaks across a neuron's membrane, helping to establish the resting potential?

In a neuron, what creates the electrochemical gradient favoring the outflow of K+ when the cell is at rest?
a. Na+/K+-ATPase
b. Voltage-gated K+ channels
c. Voltage-gated Na+ channels
d. Ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
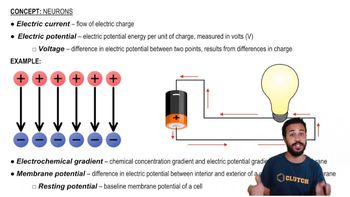
Key Concepts
Electrochemical Gradient

Na+/K+-ATPase Pump

Resting Membrane Potential
Which of these statements about myelination in neurons is/are correct? Select True or False for each statement.
T/FIt speeds propagation by increasing the density of voltage-gated channels all along the axon.
T/FMultiple sclerosis is characterized by disrupted myelination of certain neurons in the central nervous system.
T/FIt speeds propagation by preventing cations from leaking out across the membrane as they spread down the axon.
T/FIt is more commonly observed in vertebrates than in invertebrates.
Which of the following brain regions is responsible for the formation of new memories?
a. Brainstem
b. Cerebellum
c. Frontal lobe
d. Hippocampus
Explain the difference between a ligand-gated K+ channel and a voltage-gated K+ channel.
Describe the role of summation in postsynaptic cells.
