Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly. What is the mechanism of action of BTX? Identify a research technique that could be used to discover how BTX affects specific membrane proteins. Based on the graph in Question 11, what would you expect this technique to show?
Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly. What is the mechanism of action of BTX? Predict the effects of each of the following on the membrane potential of a neuron simultaneously poisoned with BTX: (a) removing extracellular sodium ions; (b) increasing the intracellular potassium ion concentration; and (c) adding tetrodotoxin from puffer fish.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Batrachotoxin Mechanism of Action
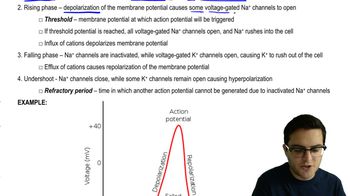
Membrane Potential
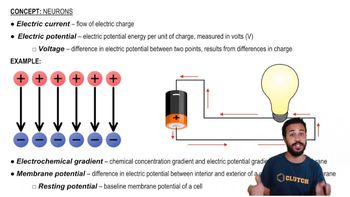
Effects of Ion Concentration Changes

Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly. What is the mechanism of action of BTX? As the graph in Question 11 shows, BTX depolarizes the membrane and prevents repolarization. What effect would this have on electrical signaling by the nervous system?
Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly. What is the mechanism of action of BTX? Like neurons, cells in skeletal and cardiac muscle also produce action potentials. Create a concept map showing how BTX could kill a mammal through its effects on nervous and muscle tissues.
Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly. What is the mechanism of action of BTX?Although BTX is a powerful antipredator poison, one snake species in Colombia eats poison dart frogs. Suggest a hypothesis that might explain how the snake is resistant to the toxin.
