Certain species of frogs in the genus Phyllobates have a powerful defensive adaptation—their skin can secrete a milky fluid that contains an extremely toxic compound called batrachotoxin (BTX). These frogs, which are found in Colombia, are known as poison dart frogs because some indigenous Colombian hunters coat the tips of their blowgun darts with the frogs' skin secretions. An animal hit by one of these darts dies quickly.
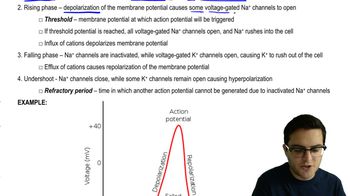
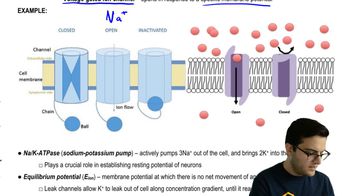
What is the mechanism of action of BTX? The graph here shows the effect of BTX on the membrane potential of a squid giant axon.
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the effect of BTX on the squid giant axon?
a. Inactivation of Na+/K+-ATPase
b. Closing of sodium channels
c. Opening of sodium channels
d. Opening of potassium channels