For each of the following, explain how structure relates to function: absorptive sections of the digestive tract; capillaries; beaks of Galápagos finches; fish gills.
Human embryonic stem cells are capable of forming all types of cells in the human body. How are these cells similar to meristem cells in plants?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Stem Cells
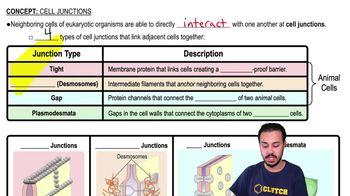
Meristem Cells

Pluripotency vs. Totipotency

The metabolic rate of a frog in summer (at 35°C) is about eight times higher than in winter (at 5°C). Compare and contrast the frog's ability to move, exchange gases, and digest food at the two temperatures. During which season will the frog require more food energy, and why?
Explain why most endotherms are homeothermic and most ectotherms are poikilothermic.
a. Consider three spheres with radii of 1 cm, 5 cm, and 10 cm. Based on what you read in the chapter, predict which sphere will have the highest surface area to volume ratio, and which sphere will have the lowest.
b. Next, calculate the surface area and the volume of each sphere. (Surface area of a sphere=4𝜋𝑟2; volume of a sphere=(4/3)𝜋𝑟3.) Plot the results on a graph with radius on the 𝑥-axis and surface area and volume on the 𝑦-axis.
c. Which sphere has the highest surface area to volume ratio? The lowest? Explain how the graph shows the relationship between size and surface area to volume ratio.
d. Now imagine that these spheres represent a small, medium, and large endothermic animal. Which animal would lose heat most rapidly? Explain using the surface area to volume ratio.
Explain why it would be impossible for a gorilla the size of King Kong to have fur. (Your answer should explain how the surface area to volume ratio of a normal-sized gorilla would compare to Kong's; relate this to the role of surface area and volume in heat generation and heat transfer, and consider the function of fur.)
The dinosaur Apatosaurus (Brontosaurus) is one of the largest terrestrial animals that ever lived—over 20 m in length and weighing over 20 metric tons. Is it more likely that Apatosaurus was homeothermic or poikilothermic? Explain.
