Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Operon Structure
An operon is a cluster of genes that are transcribed together as a single mRNA molecule, typically under the control of a single promoter. This arrangement allows for coordinated regulation of genes that encode proteins with related functions, facilitating efficient gene expression in response to environmental changes.
Recommended video:
Gene Regulation
Gene regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the expression of genes, ensuring that the right genes are expressed at the right times. In the case of operons, regulatory elements such as promoters and operators play crucial roles in turning genes on or off in response to specific signals, such as the presence of lactose in the environment.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression
Lactose Metabolism in E. coli
In E. coli, lactose metabolism involves several genes, including lacZ, lacY, and lacA, which are responsible for the breakdown and transport of lactose. These genes are organized in the lac operon, allowing the bacterium to efficiently utilize lactose as an energy source when glucose is scarce, demonstrating the operon's role in metabolic adaptation.
Recommended video:
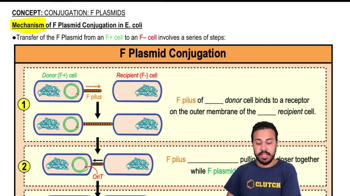
Mechanism of F Plasmid Conjugation in E. coli