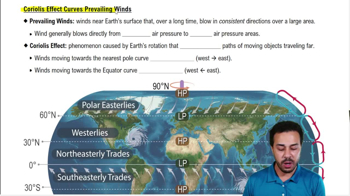
<Image>
Eating even a single death cap mushroom (Amanita phalloides) can be fatal due to a compound called α-amanitin, a toxin that inhibits transcription.
Toxins like α-amanitin are used for research in much the same way as null mutants (Chapter 16)—to disrupt a process and see what happens when it no longer works. Researchers examined the ability of α-amanitin to inhibit different RNA polymerases. They purified RNA polymerases I, II, and III from rat liver, incubated the enzymes with different concentrations of α-amanitin, and then tested their activity. The results of this experiment are shown here. These findings suggest that cells treated with α-amanitin will have a reduced level of:
a. tRNAs
b. rRNAs
c. snRNAs
d. mRNAs