The middle ear converts a. air pressure waves to fluid pressure waves. b. air pressure waves to nerve impulses. c. fluid pressure waves to nerve impulses. d. pressure waves to hair cell movements.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Middle Ear Anatomy

Sound Wave Transmission
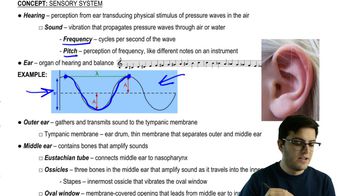
Auditory Signal Processing

During the contraction of a vertebrate skeletal muscle fiber, calcium ions a. break cross-bridges as a cofactor in hydrolysis of ATP. b. bind with troponin, changing its shape so that the myosin-binding sites on actin are exposed. c. transmit action potentials from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber. d. spread action potentials through the T tubules.
The transduction of sound waves into action potentials occurs a. in the tectorial membrane as it is stimulated by hair cells. b. when hair cells are bent against the tectorial membrane, causing them to depolarize and release neurotransmitter that stimulates sensory neurons. c. as the basilar membrane vibrates at different frequencies in response to the varying volume of sounds. d. within the middle ear as the vibrations are amplified by the malleus, incus, and stapes.
