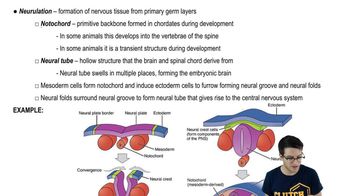
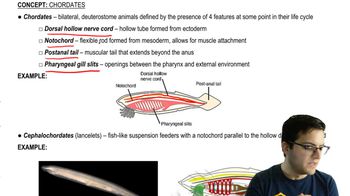
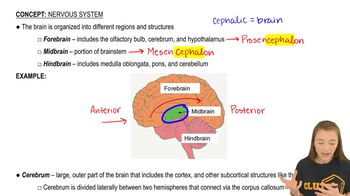
Textbook Question
Living vertebrates can be divided into two major clades. Select the appropriate pair. a. the chordates and the tetrapods b. the urochordates and the cephalochordates c. the cyclostomes and the gnathostomes d. the marsupials and the eutherians
708
views
1
rank