According to the phylogeny presented in this chapter, which protists are in the same eukaryotic supergroup as plants? a. green algae b. dinoflagellates c. red algae d. both A and C
Ch. 28 - Protists
Chapter 28, Problem 7
EVOLUTION CONNECTION • DRAW IT Medical researchers seek to develop drugs that can kill or restrict the growth of human pathogens yet have few harmful effects on patients. These drugs often work by disrupting the metabolism of the pathogen or by targeting its structural features. Draw and label a phylogenetic tree that includes an ancestral prokaryote and the following groups of organisms: Excavata, SAR, Archaeplastida, Unikonta, and, within Unikonta, amoebozoans, animals, choanoflagellates, fungi, and nucleariids. Based on this tree, hypothesize whether it would be most difficult to develop drugs to combat human pathogens that are prokaryotes, protists, animals, or fungi. (You do not need to consider the evolution of drug resistance by the pathogen.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Draw the base of the phylogenetic tree starting with the ancestral prokaryote at the root.
From the ancestral prokaryote, draw a branch leading to the Excavata group.
Next, draw a branch from the ancestral prokaryote leading to the SAR group.
Draw another branch from the ancestral prokaryote leading to the Archaeplastida group.
From the ancestral prokaryote, draw a branch leading to the Unikonta group, and within Unikonta, create sub-branches for amoebozoans, animals, choanoflagellates, fungi, and nucleariids.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on their genetic or physical characteristics. It illustrates how different groups of organisms are related through common ancestors, allowing researchers to visualize evolutionary pathways. In this context, the tree will help identify the evolutionary distance between human pathogens and other organisms, which is crucial for understanding drug development challenges.
Recommended video:

Building Phylogenetic Trees Example 2
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes have a defined nucleus and complex cellular structures. This distinction is significant in drug development, as prokaryotic pathogens (like bacteria) may have different metabolic pathways and structural features compared to eukaryotic pathogens (like fungi and protists). Understanding these differences is essential for targeting drugs effectively without harming human cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course
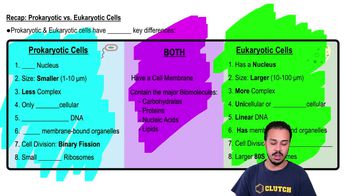
Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Drug Targeting Mechanisms
Drug targeting mechanisms refer to the strategies used to design pharmaceuticals that specifically affect pathogens while minimizing harm to human cells. These mechanisms can involve disrupting metabolic processes unique to the pathogen or targeting structural features that differ from those in human cells. The effectiveness of these strategies can vary significantly between prokaryotes, protists, animals, and fungi, influencing the difficulty of developing effective treatments.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Prey Defense Mechanisms
Related Practice
Textbook Question
489
views
Textbook Question
In a life cycle with alternation of generations, multicellular haploid forms alternate with a. unicellular haploid forms. b. unicellular diploid forms. c. multicellular haploid forms. d. multicellular diploid forms.
805
views
Textbook Question
Based on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 28.2, which of the following statements is correct? a. The most recent common ancestor of Excavata is older than that of SAR. b. The most recent common ancestor of SAR is older than that of Unikonta. c. The most basal (first to diverge) eukaryotic supergroup cannot be determined. d. Excavata is the most basal eukaryotic supergroup.
492
views
