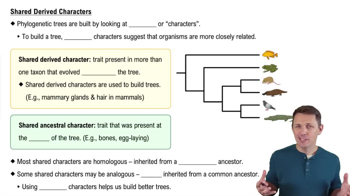
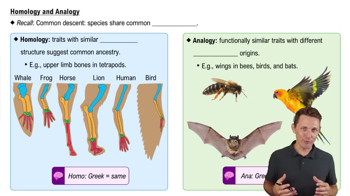
To apply parsimony to constructing a phylogenetic tree
a. Choose the tree that assumes all evolutionary changes are equally probable
b. Choose the tree in which the branch points are based on as many shared derived characters as possible
c. Choose the tree that represents the fewest evolutionary changes, in either DNA sequences or morphology
d. Choose the tree with the fewest branch points