Which of the following tools of DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use? a. electrophoresis—separation of DNA fragments b. DNA ligase—cutting DNA, creating sticky ends of restriction fragments c. DNA polymerase—polymerase chain reaction to amplify sections of DNA d. reverse transcriptase—production of cDNA from mRNA
Ch. 20 - DNA Tools and Biotechnology
Chapter 20, Problem 1
In DNA technology, the term vector can refer to a. the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments. b. the sticky end of a DNA fragment. c. a SNP marker. d. a plasmid used to transfer DNA into a living cell.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the term 'vector' in the context of DNA technology. A vector is generally a vehicle used to transfer genetic material from one cell to another.
Eliminate options that do not fit the definition of a vector. Option a, the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments, is known as a restriction enzyme, not a vector.
Option b, the sticky end of a DNA fragment, refers to the overhanging ends of DNA that are exposed after cutting by restriction enzymes. These are not vectors but sites for DNA ligase to act.
Option c, a SNP marker, stands for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, which is a type of genetic marker used in mapping and is not a vector.
Conclude that option d, a plasmid used to transfer DNA into a living cell, fits the definition of a vector in DNA technology. Plasmids are circular DNA molecules used in genetic engineering to transport genetic material into cells.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vectors in Genetic Engineering
In genetic engineering, a vector is a vehicle used to transfer genetic material into a host cell. Common vectors include plasmids, which are small circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently within a bacterial cell. Vectors are essential for cloning, gene expression, and gene therapy, as they facilitate the introduction of foreign DNA into target cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genetic Code
Plasmids
Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA molecules found in bacteria and some eukaryotes. They often carry genes that provide advantageous traits, such as antibiotic resistance. In biotechnology, plasmids are engineered to include specific genes of interest, allowing researchers to manipulate and study gene function or produce proteins in host organisms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
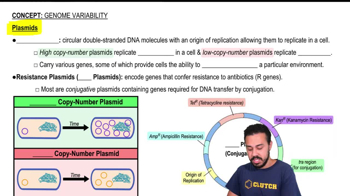
Plasmids
Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes, or restriction endonucleases, are proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences, creating fragments with 'sticky' or 'blunt' ends. These enzymes are crucial in molecular cloning, as they allow scientists to cut both the vector and the DNA of interest to create compatible ends for ligation. This process is fundamental for inserting genes into vectors for further study or application.
Recommended video:
Guided course

1a) Use Restriction Enzymes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
648
views
Textbook Question
Plants are more readily manipulated by genetic engineering than are animals because a. plant genes do not contain introns. b. more vectors are available for transferring recombinant DNA into plant cells. c. a somatic plant cell can often give rise to a complete plant. d. plant cells have larger nuclei.
1409
views
Textbook Question
A paleontologist has recovered a bit of tissue from the 400-year-old preserved skin of an extinct dodo (a bird). To compare a specific region of the DNA from a sample with DNA from living birds, which of the following would be most useful for increasing the amount of dodo DNA available for testing? a. SNP analysis b. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) c. electroporation d. gel electrophoresis
1263
views
