The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation is the a. oxidation of glucose and other organic compounds. b. flow of electrons down the electron transport chain. c. H+ concentration gradient across the membrane holding ATP synthase. d. transfer of phosphate to ADP.
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
Chapter 9, Problem 2
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule? a. the citric acid cycle b. the electron transport chain c. glycolysis d. reduction of pyruvate to lactate
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the metabolic pathways involved in both fermentation and cellular respiration. Fermentation is an anaerobic process, while cellular respiration can be aerobic.
Recall that glycolysis is the initial step in the breakdown of glucose and occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Understand that the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain are parts of aerobic respiration and do not occur in anaerobic fermentation.
Recognize that the reduction of pyruvate to lactate specifically occurs during lactic acid fermentation, not in all types of fermentation or in aerobic respiration.
Conclude that glycolysis is the only pathway among the options that is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
49sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process. It occurs in the cytoplasm and is the first step in both fermentation and cellular respiration, making it a universal pathway for energy extraction from glucose.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Glycolysis
Fermentation
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows cells to generate energy without oxygen. It follows glycolysis when oxygen is scarce, converting pyruvate into various end products, such as lactic acid or ethanol, while regenerating NAD+ to sustain glycolysis.
Recommended video:
Guided course
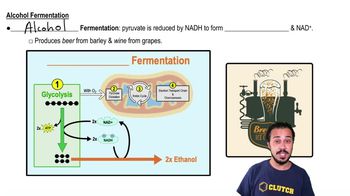
Alcohol Fermentation
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is an aerobic process that fully oxidizes glucose to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. It includes glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain, allowing for a more efficient energy yield compared to fermentation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Cellular Respiration
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2627
views
Textbook Question
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is a. oxygen. b. water. c. NAD+. d. pyruvate.
1763
views
Textbook Question
In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions a. are the source of energy driving prokaryotic ATP synthesis. b. provide the energy that establishes the proton gradient. c. reduce carbon atoms to carbon dioxide. d. are coupled via phosphorylated intermediates to endergonic processes
1572
views
Textbook Question
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate+NADH+H+→Lactate+NAD+ a. oxygen b. NADH c. lactate d. pyruvate
3598
views
