Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Endomembrane System
The endomembrane system is a network of membranes within eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes structures such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles. This system plays a crucial role in cellular organization and function, facilitating communication and transport between different organelles.
Recommended video:
Endomembrane System: Protein Secretion
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a key organelle in the endomembrane system, responsible for processing and packaging proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It modifies these molecules by adding carbohydrate or phosphate groups and sorts them for transport to their final destinations, either within the cell or for secretion. Its structure consists of stacked, flattened membrane sacs called cisternae.
Recommended video:
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
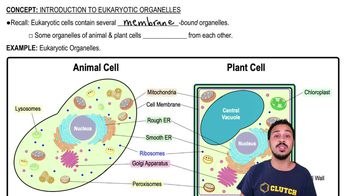
Eukaryotic cells contain various organelles, each with specific functions that contribute to the cell's overall operation. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Understanding the roles of these organelles is essential for grasping cellular processes and the distinctions between different cell types.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance