Textbook Question
Which structure is part of the endomembrane system?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Chloroplast
d. Centrosome
2366
views
1
rank

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
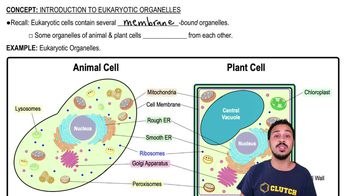


Which structure is part of the endomembrane system?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Chloroplast
d. Centrosome
Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Ribosome
c. Nuclear envelope
d. Chloroplast
Cyanide binds to at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the
a. Mitochondria.
b. Ribosomes.
c. Peroxisomes.
d. Lysosomes.
Which cell would be best for studying lysosomes?
a. Muscle cell
b. Nerve cell
c. Bacterial cell
d. Phagocytic white blood cell