Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Extraembryonic Membranes
Extraembryonic membranes are structures that develop outside the embryo in amniotes, including chickens, to provide protection and support. These membranes include the amnion, chorion, yolk sac, and allantois, which collectively facilitate gas exchange, waste removal, and nutrient transfer, allowing eggs to be laid in terrestrial environments without the need for water.
Recommended video:
Yolk
The yolk is a nutrient-rich part of the egg that provides essential nourishment to the developing embryo. In chickens, the yolk contains proteins, fats, and vitamins necessary for growth, enabling the embryo to develop in a self-contained environment without external food sources, which is crucial for survival in arid conditions.
Recommended video:
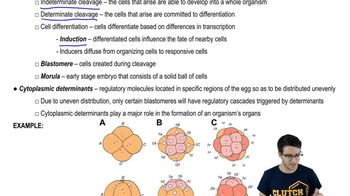
Cleavage
Cleavage is the series of rapid cell divisions that occur immediately after fertilization, leading to the formation of a multicellular embryo. In chickens, cleavage is adapted to occur within the confines of the egg, allowing the embryo to develop efficiently in a terrestrial setting, independent of water-based environments.
Recommended video:
Cleavage and Blastulation