Which of the following is an adaptation that enhances the uptake of water and minerals by roots? a. mycorrhizae b. pumping through plasmodesmata c. active uptake by vessel elements d. rhythmic contractions by cells in the root cortex
 Campbell 12th Edition
Campbell 12th Edition Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
Ch. 36 - Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants Problem 4
Problem 4Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because a. the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded. b. accumulation of CO2 in the leaf inhibits enzymes. c. stomata close, preventing CO2 from entering the leaf. d. photolysis, the water-splitting step of photosynthesis, cannot occur when there is a water deficiency.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Photosynthesis

Stomata
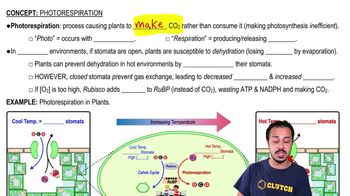
Photolysis
Which structure or compartment is part of the symplast? a. the interior of a vessel element b. the interior of a sieve tube c. the cell wall of a mesophyll cell d. an extracellular air space
Movement of phloem sap from a source to a sink a. occurs through the apoplast of sieve-tube elements. b. depends ultimately on the activity of proton pumps. c. depends on tension, or negative pressure potential. d. results mainly from diffusion.
What would enhance water uptake by a plant cell? a. decreasing the Ψ of the surrounding solution b. positive pressure on the surrounding solution c. the loss of solutes from the cell d. increasing the Ψ of the cytoplasm
A plant cell with a ΨS of −0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a ΨS of −0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a a. ΨP of +0.65 MPa. b. Ψ of −0.65 MPa. c. ΨP of +0.35 MPa. d. ΨP of 0 MPa.
Compared with a cell with few aquaporin proteins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporin proteins will a. have a faster rate of osmosis. b. have a lower water potential. c. have a higher water potential. d. accumulate water by active transport.