All the organisms on your campus make up a. an ecosystem. b. a community. c. a population. d. a taxonomic domain.
 Campbell 12th Edition
Campbell 12th Edition Ch. 1 - Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
Ch. 1 - Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry Problem 4
Problem 4A controlled experiment is one that a. proceeds slowly enough that a scientist can make careful records of the results. b. tests experimental and control groups in parallel. c. is repeated many times to make sure the results are accurate. d. keeps all variables constant.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
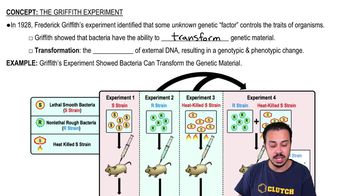
Controlled Experiment
Variables

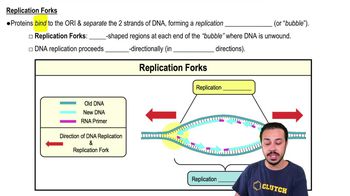
Replication
Systems biology is mainly an attempt to a. analyze genomes from different species. b. simplify complex problems by reducing the system into smaller, less complex units. c. understand the behavior of entire biological systems by studying interactions among its component parts. d. build high-throughput machines for the rapid acquisition of biological data.
Which of the following best demonstrates the unity among all organisms? a. emergent properties b. descent with modification c. the structure and function of DNA d. natural selection
Which of the following statements best distinguishes hypotheses from theories in science? a. Theories are hypotheses that have been proved. b. Hypotheses are guesses; theories are correct answers. c. Hypotheses usually are relatively narrow in scope; theories have broad explanatory power. d. Theories are proved true; hypotheses are often contradicted by experimental results.
Which of the following is an example of qualitative data? a. The fish swam in a zigzag motion. b. The contents of the stomach are mixed every 20 seconds. c. The temperature decreased from 20°C to 15°C. d. The six pairs of robins hatched an average of three chicks each.
Which sentence best describes the logic of scientific inquiry? a. If I generate a testable hypothesis, tests and observations will support it. b. If my prediction is correct, it will lead to a testable hypothesis. c. If my observations are accurate, they will support my hypothesis. d. If my hypothesis is correct, I can expect certain test results.