Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
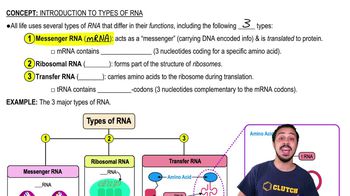
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ribosomal RNA is a type of RNA that is a fundamental component of ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis. rRNA sequences are highly conserved across different species, making them useful for phylogenetic studies. By comparing rRNA sequences, scientists can infer evolutionary relationships and classify organisms based on genetic similarities and differences.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Types of RNA
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relationships among biological entities, often using genetic data to construct evolutionary trees. This field helps in understanding how different species are related through common ancestry. The analysis of rRNA sequences is a common method in phylogenetics, allowing researchers to identify major lineages and divergences among groups such as prokaryotes, fungi, and protists.
Recommended video:
Building Phylogenetic Trees Example 2
Taxonomic Relationships
Taxonomic relationships refer to the classification and organization of living organisms based on shared characteristics and evolutionary history. Understanding these relationships helps clarify how different groups, such as fungi, animals, and plants, are related. Recent studies using rRNA comparisons have revealed surprising connections, such as the closer relationship between fungi and animals compared to plants, challenging traditional classifications.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance