Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Prefertilization Barriers
Prefertilization barriers are mechanisms that prevent mating or fertilization between different species. These barriers can be behavioral, temporal, mechanical, or ecological, ensuring that species remain distinct by inhibiting successful reproduction before fertilization occurs.
Recommended video:
Behavioral Isolation
Behavioral isolation occurs when two species have different mating behaviors or rituals that prevent them from recognizing each other as potential mates. For example, if one species has a specific courtship display that the other does not respond to, they will not mate, thus serving as a prefertilization barrier.
Recommended video:
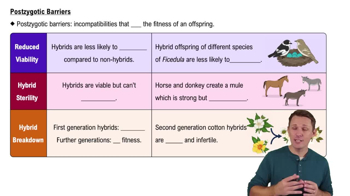
Hybrid Viability and Fertility
Hybrid viability and fertility refer to the ability of hybrid offspring to survive and reproduce. While some hybrids may be produced, they can be sterile or have reduced fitness, which affects their ability to contribute to the gene pool of either parent species, highlighting the importance of reproductive barriers.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance