Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. In the context of human populations, it highlights that there is often more genetic variation within so-called racial groups than between them, suggesting that traditional racial classifications do not accurately reflect biological differences.
Recommended video:
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are variations at a single position in a DNA sequence among individuals. Geneticists use SNPs to trace ancestry and population structure, but the presence of specific SNPs does not necessarily correlate with racial classifications, indicating that genetic traits are not confined to traditional racial boundaries.
Recommended video:
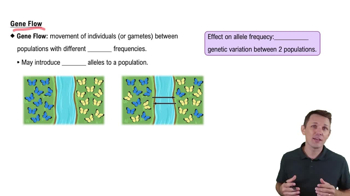
Gene Flow and Mixing
Gene flow refers to the transfer of genetic material between populations, which can occur through migration and interbreeding. The historical mixing of human populations has led to a complex genetic landscape, undermining the concept of distinct biological races and supporting the idea that all humans share a common ancestry with overlapping genetic traits.
Recommended video: