Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. This process involves the coordinated activity of osteoclasts, which break down bone, and osteoblasts, which build new bone. If remodeling did not occur, bones would not adapt to stress or repair micro-damage, leading to potential structural weaknesses.
Recommended video:
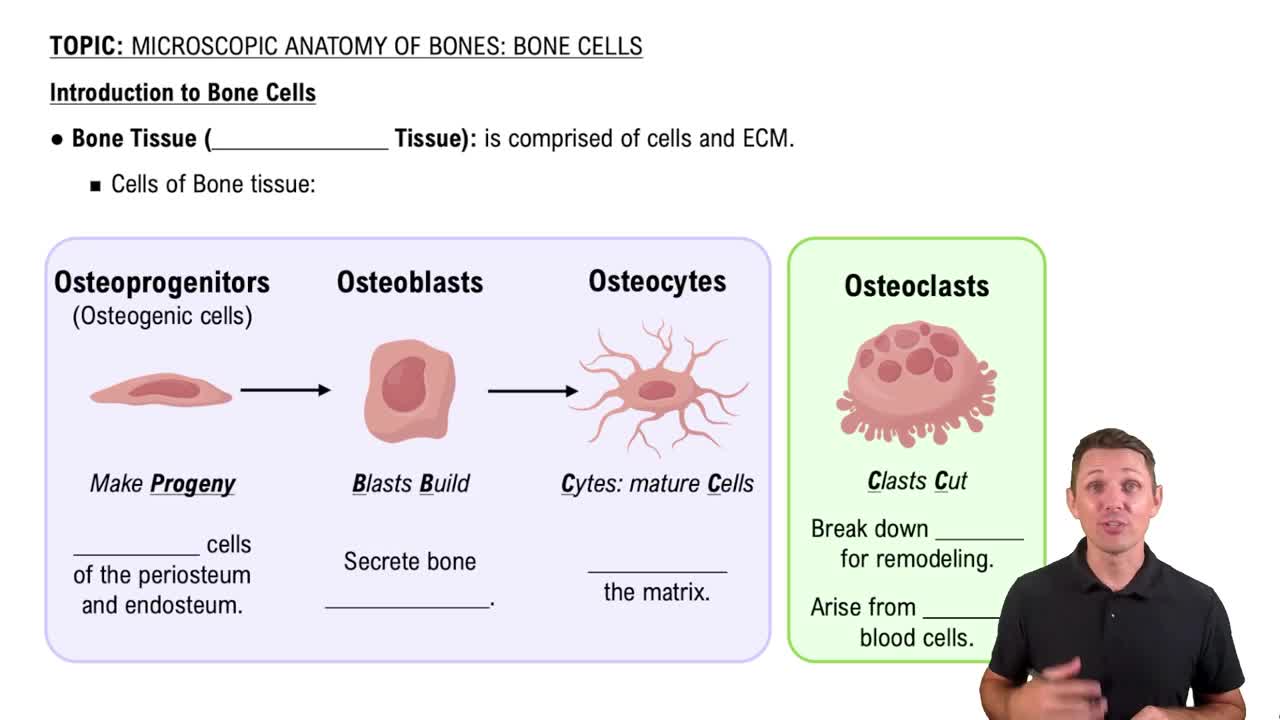
Introduction to Bone Cells
Long Bone Structure
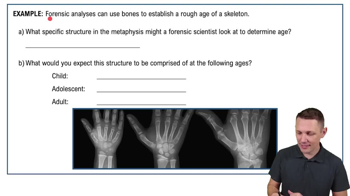
Long bones, such as the femur or humerus, have a specific structure characterized by a diaphysis (shaft) and epiphyses (ends). They are primarily composed of compact bone, which provides strength, and spongy bone, which reduces weight. The growth plates at the ends of long bones close after adolescence, and without remodeling, the bone would retain its adolescent form, potentially leading to abnormal growth or density.
Recommended video:
Gross Anatomy of Bones - Structure of a Long Bone Example 1
Adolescence and Bone Development
Adolescence is a critical period for bone development, marked by rapid growth and changes in bone density. During this time, bones undergo significant changes in size and shape due to hormonal influences and physical activity. If bone remodeling did not occur at the end of adolescence, the bones would not adapt to the changes in body size and mechanical demands, potentially resulting in a less resilient skeletal structure.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Human Development
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance