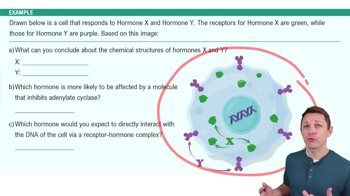
Textbook Question
Answer questions 5 through 10 by choosing responses from the following:
a. ammonium ions
b. bicarbonate
c. calcium
d. chloride
e. hydrogen ions
f. magnesium
g. phosphate
h. potassium
i. sodium
j. water
Substance regulated by ADH's effects on the renal tubules.
246
views