Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
MALT refers to collections of lymphoid tissues found in mucosal surfaces, playing a crucial role in the immune response. It includes structures such as the tonsils, Peyer's patches in the intestines, and appendix follicles, which help protect against pathogens entering through mucosal surfaces.
Recommended video:
Secondary Lymphoid Organs: MALT Example 1
Tonsils
Tonsils are lymphoid tissues located in the throat that act as the first line of defense against ingested or inhaled pathogens. They are part of MALT and help in the production of antibodies and the activation of immune responses.
Recommended video:
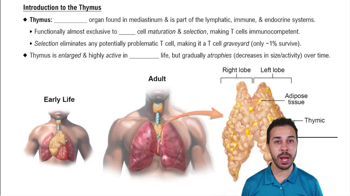
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized organ located in the chest that is essential for the development of T-cells, a type of white blood cell crucial for adaptive immunity. Unlike MALT, the thymus is not associated with mucosal surfaces and does not function as a barrier against pathogens.
Recommended video:
Introduction to the Thymus
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 20 The Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues
Ch. 20 The Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Problem 9
Problem 9 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance