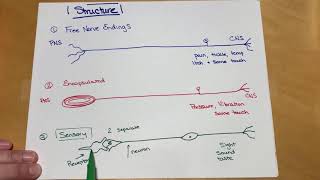
13. The Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory Receptor Classification by Modality
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which receptor type would you expect to find on the tongue, allowing us to taste?
1460views23rank - Multiple ChoiceWhich type of sensory receptor is stimulated by touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch?1611views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following have nonencapsulated (free) nerve endings?1361views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceProprioceptors advise the brain of __________.1323views1rank
- Textbook Question
The larger the receptive field, the
(a) Larger the stimulus needed to stimulate a sensory receptor
(b) Fewer sensory receptors there are
(c) Harder it is to locate the exact point of stimulation
(d) Larger the area of the somatosensory cortex in the brain that deals with the area
(e) Closer together the receptor cells
858views - Textbook Question
_______ receptors are normally inactive, but become active for a short time whenever there is a change in the modality that they monitor.
593views - Textbook Question
Match the receptor type in column B to the correct description in column A.
Column A
______ (1) Pain, itch, and temperature receptors
______ (2) Contains intrafusal fibers and anulospiral and flower spray endings
______ (3) Discriminative touch receptor in hairless skin (fingertips)
______ (4) Contains receptor endings wrapped around thick collagen bundles
______ (5) Rapidly adapting deep-pressure receptor
______ (6) Slowly adapting deep-pressure receptor
Column B
a. Bulbous corpuscles
b. Tendon organ
c. Muscle spindle
d. Free nerve endings
e. Lamellar corpuscle
f. Tactile corpuscle
744views - Textbook Question
The CNS interprets information entirely on the basis of the
(a) Number of action potentials that it receives
(b) Kind of action potentials that it receives
(c) Line over which sensory information arrives
(d) Intensity of the sensory stimulus
(e) Number of sensory receptors that are stimulated
619views