3. Energy & Cell Processes
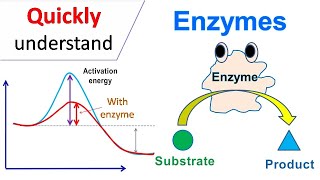
Enzymes
3. Energy & Cell Processes
Enzymes
Additional 7 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following are examples of the functions of enzymes?
3405views22rank - Multiple Choice
Which characteristics are likely associated with an enzyme isolated from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acidic.
2891views25rank - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is changed by the presence of an enzyme in a reaction? and1027views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following statements about enzymes is/are true?2498views
- Textbook QuestionAdd labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates the breakdown of a disaccharide inside a cell.850views
- Textbook QuestionHow does pH affect enzyme-catalyzed reactions? a. Protons serve as substrates for most reactions. b. Energy stored in protons is used to drive endergonic reactions. c. Proton concentration increases the kinetic energy of the reactants, enabling them to reach their transition state. d. The concentration of protons affects an enzyme's folded structure and reactivity.1207views
- Textbook QuestionWhich of the following is a false statement regarding enzymes? a. Enzymes are proteins that speed up metabolic reactions; b. Enzymes have specific substrates; c. Enzymes supply ATP to their substrates; d. An enzyme may be used many times.2004views
- Textbook QuestionIf an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to a. add more of the enzyme. b. heat the solution to 90°C. c. add more substrate. d. add a noncompetitive inhibitor.1759views