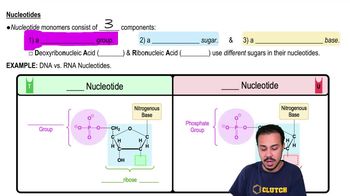
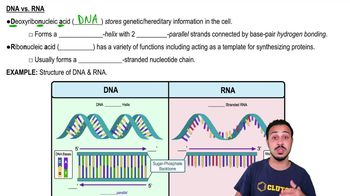
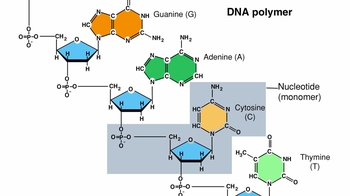
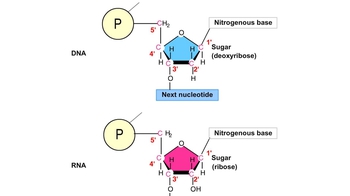
2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
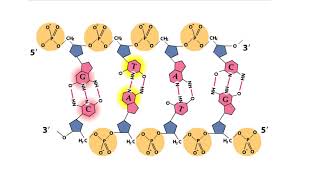
Nucleic Acids
2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
Nucleic Acids
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Additional 6 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 9 of 9 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
5945views62rank - Multiple Choice
The four nitrogenous bases commonly found if DNA are:
7101views58rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about DNA structure is true?
7248views61rank - Multiple ChoiceA glucose molecule is to starch as __________.2813views
- Textbook QuestionWhat are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA?a. cytosine, guanine, thymine, uracil (C, G, T, U)b. adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine (A, C, G, T)c. adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (A, C, G, U)d. alanine, cysteine, glycine, threonine (A, C, G, T)2280views
- Textbook QuestionWhat determines the primary structure of a DNA molecule?a. stem-and-loop configurationb. complementary base pairingc. deoxyribonucleotide sequenced. hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding2131views
- Textbook QuestionEvaluate the following statements related to the synthesis of nucleic acids. Select True or False for each statement.T/F Ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of a DNA strand.T/F Polymerization of nucleic acids occurs by the formation of phosphodiester bonds.T/F Complementary pairing between sugars is required for copying nucleic acids.T/F Strands in a double helix are synthesized in an antiparallel orientation.1442views
- Textbook QuestionSingle strands of nucleic acids are directional, meaning that there are two different ends. What functional groups define the two different ends of a strand?2640views