Textbook Question
For each function, give the amplitude, period, vertical translation, and phase shift, as applicable.
y = 3 - ¼ cos ⅔ x
214
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
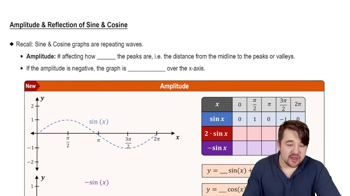

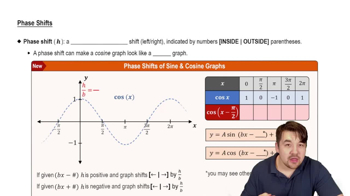
For each function, give the amplitude, period, vertical translation, and phase shift, as applicable.
y = 3 - ¼ cos ⅔ x
Graph each function over a one-period interval.
y = 3 sec [(1/4)x]
Match each function with its graph in choices A–I. (One choice will not be used.)
y = cos (x - π/4)
A. <IMAGE> B. <IMAGE> C. <IMAGE>
D. <IMAGE> E. <IMAGE> F. <IMAGE>
G. <IMAGE> H. <IMAGE> I. <IMAGE>
For each function, give the amplitude, period, vertical translation, and phase shift, as applicable.
y = -sin (x - 3π/4)
Graph each function over the interval [-2π, 2π]. Give the amplitude. See Example 1.
y = 2 cos x
Graph each function over a one-period interval. See Examples 1–3.
y = tan 4x