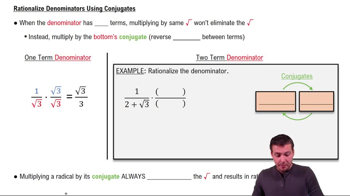
0. Review of College Algebra
Rationalizing Denominators
0. Review of College Algebra
Rationalizing Denominators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Rationalize the denominator.
1739views15rank - Multiple Choice
Rationalize the denominator.
1270views21rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Rationalize the denominator and simplify the radical expression.
1224views7rank - Multiple Choice
Rationalize the denominator and simplify the radical expression.
1039views7rank - Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Perform the operations mentally, and write the answers without doing intermediate steps.√25 + √64742views
- Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Perform the operations mentally, and write the answers without doing intermediate steps.√6 • √6760views
- Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Perform the operations mentally, and write the answers without doing intermediate steps.(√28 - √14) (√28 + √14)757views
- Textbook QuestionFind each square root. SeeExample 1.√100823views