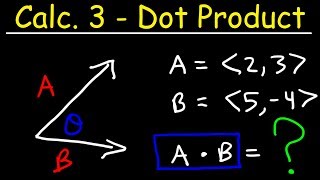
8. Vectors
Dot Product
8. Vectors
Dot Product
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 8 of 8 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
If vectors and , calculate .
443views - Multiple Choice
If vectors and , calculate .
423views - Multiple Choice
If vectors , , and , calculate .
413views1rank - Multiple Choice
If vectors and , and , determine the angle between vectors and .
425views - Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the given vectors to find v⋅w and v⋅v.v = 3i + j, w = i + 3j709views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, use the given vectors to find v⋅w and v⋅v.v = 5i - 4j, w = -2i - j625views
- Textbook Question
In Exercises 1–8, use the given vectors to find v⋅w and v⋅v. v = -6i - 5j, w = -10i - 8j
672views - Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 5–8, letv = -5i + 2j and w = 2i - 4jFind the specified vector, scalar, or angle.v ⋅ w600views