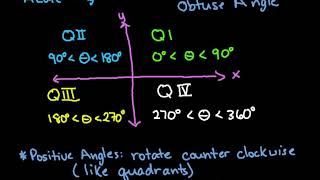Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
1. Measuring Angles
Angles in Standard Position
Problem 91
Textbook Question
Textbook Question(Modeling) Length of a Sag Curve When a highway goes downhill and then uphill, it has a sag curve. Sag curves are designed so that at night, headlights shine sufficiently far down the road to allow a safe stopping distance. See the figure. S and L are in feet. The minimum length L of a sag curve is determined by the height h of the car's headlights above the pavement, the downhill grade θ₁ < 0°, the uphill grade θ₂ > 0°, and the safe stopping distance S for a given speed limit. In addition, L is dependent on the vertical alignment of the headlights. Headlights are usually pointed upward at a slight angle α above the horizontal of the car. Using these quantities, for a 55 mph speed limit, L can be modeled by the formula (θ₂ - θ₁)S² L = ————————— , 200(h + S tan α) where S < L. (Data from Mannering, F., and W. Kilareski, Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis, Second Edition, John Wiley and Sons.) Compute length L, to the nearest foot, if h = 1.9 ft, α = 0.9°, θ₁ = -3°, θ₂ = 4°, and S = 336 ft.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sag Curve Design
A sag curve is a vertical curve that connects a downhill slope to an uphill slope on a roadway. It is designed to ensure that vehicles can safely navigate the transition while maintaining visibility, particularly at night. The curve's geometry is influenced by factors such as the height of headlights, road grades, and stopping distances, which are critical for ensuring driver safety.
Recommended video:

Example 1
Trigonometric Functions in Road Design
Trigonometric functions, particularly tangent, are used in road design to relate angles of elevation and depression to distances. In the context of sag curves, the angle of the headlights above the horizontal (α) affects how far ahead a driver can see. The formula incorporates these angles to calculate the necessary length of the sag curve, ensuring that the headlights illuminate the road adequately.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Mathematical Modeling of Road Safety
Mathematical modeling in road safety involves using equations to predict and ensure safe driving conditions. The formula provided for calculating the length of a sag curve incorporates various parameters such as grades, stopping distance, and headlight height. Understanding how to manipulate and apply this formula is essential for engineers to design safe roadways that accommodate different driving speeds and conditions.
Recommended video:

Review of Triangles

 5:50m
5:50mWatch next
Master Drawing Angles in Standard Position with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice