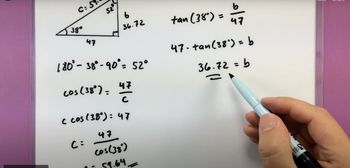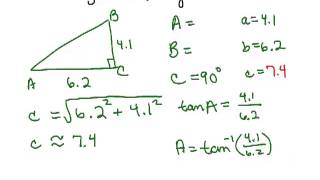Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
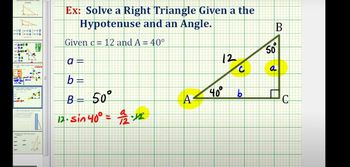
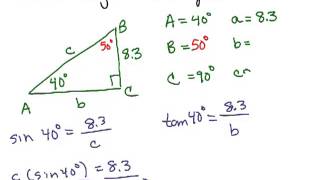
Solving Right Triangles
Problem 13
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 13–16, the graph of a cotangent function is given. Select the equation for each graph from the following options:
y = cot(x + π/2), y = cot(x + π), y = −cot x, y= −cot(x − π/2).

 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cotangent Function
The cotangent function, denoted as cot(x), is the reciprocal of the tangent function. It is defined as cot(x) = cos(x)/sin(x). The graph of the cotangent function has vertical asymptotes where sin(x) = 0, which occurs at integer multiples of π. Understanding the basic shape and periodicity of the cotangent function is essential for analyzing its transformations.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Cotangent Graph
Transformations of Functions
Transformations of functions involve shifting, reflecting, stretching, or compressing the graph of a function. For the cotangent function, horizontal shifts can be represented by adding or subtracting a constant inside the function's argument, such as cot(x + π/2). Recognizing how these transformations affect the graph is crucial for identifying the correct equation from a given graph.
Recommended video:

Domain and Range of Function Transformations
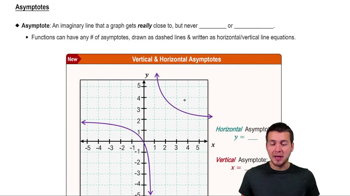
Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes are lines that a graph approaches but never touches or crosses. For the cotangent function, vertical asymptotes occur at x = nπ, where n is an integer. In the provided graph, the locations of these asymptotes help determine the function's behavior and are key indicators for selecting the correct cotangent equation based on the graph's features.
Recommended video:
Asymptotes

 4:18m
4:18mWatch next
Master Finding Missing Side Lengths with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice