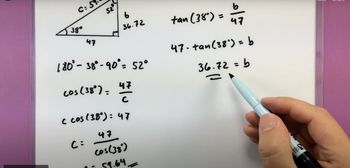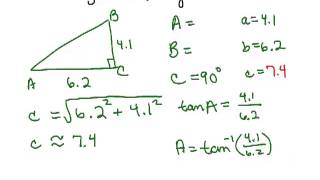Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
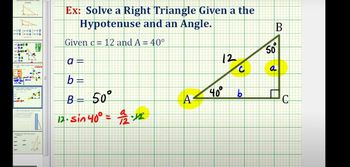
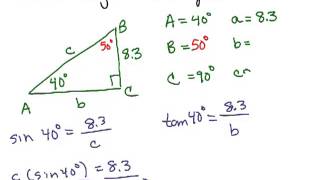
Solving Right Triangles
Problem 3d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Match each equation in Column I with the appropriate right triangle in Column II. In each case, the goal is to find the value of x. I II 1. A. B. C. 2. 3. x = 5 tan 38° D. E. F. 4. 5. 6.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios are relationships between the angles and sides of a right triangle. The primary ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent, defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse to a given angle. Understanding these ratios is essential for solving problems involving right triangles, as they allow for the calculation of unknown side lengths or angles.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Tangent Function
The tangent function is one of the primary trigonometric functions, defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side in a right triangle. It is often represented as tan(θ) = opposite/adjacent. In the context of the given question, using the tangent function allows for the calculation of the side lengths when an angle and one side length are known.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Tangent Graph
Right Triangle Properties
Right triangles have specific properties that simplify the analysis of their angles and sides. The Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, is fundamental. Additionally, the angles in a right triangle always sum to 180 degrees, with one angle being 90 degrees, which is crucial for determining unknown angles or sides in trigonometric problems.
Recommended video:
30-60-90 Triangles

 4:18m
4:18mWatch next
Master Finding Missing Side Lengths with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice