Find each exact function value. See Example 2. cos (―4π/3)
Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 45m
- 1. Measuring Angles40m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
Defining the Unit Circle
Problem 27
Textbook Question
Find each exact function value. See Example 2.
sin (-4π/3)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recognize the angle given is \( \frac{4\pi}{3} \), which is in radians. This angle is more than \( \pi \) (or 180°), so it lies in the third quadrant of the unit circle.
Recall that the sine function is negative in the third quadrant because the y-coordinate of points on the unit circle is negative there.
Find the reference angle for \( \frac{4\pi}{3} \) by subtracting \( \pi \) from it: \( \frac{4\pi}{3} - \pi = \frac{4\pi}{3} - \frac{3\pi}{3} = \frac{\pi}{3} \).
Use the known sine value for the reference angle \( \frac{\pi}{3} \), which is \( \sin\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right) = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \).
Since the original angle is in the third quadrant where sine is negative, the exact value of \( \sin\left(\frac{4\pi}{3}\right) \) is \( -\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \).
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Unit Circle and Radian Measure
The unit circle is a circle with radius 1 centered at the origin, used to define trigonometric functions for all angles. Radian measure relates the angle to the length of the arc on the unit circle, where 2π radians equal 360 degrees. Understanding the position of 4π/3 radians on the unit circle helps determine the sine value.
Recommended video:

Introduction to the Unit Circle
Sine Function on the Unit Circle
The sine of an angle corresponds to the y-coordinate of the point where the terminal side of the angle intersects the unit circle. For angles in different quadrants, sine values can be positive or negative. Knowing the quadrant of 4π/3 helps identify the sign and exact value of sin(4π/3).
Recommended video:
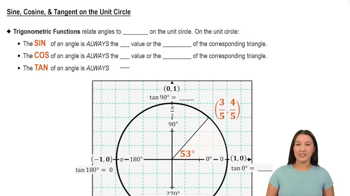
Sine, Cosine, & Tangent on the Unit Circle
Reference Angles
A reference angle is the acute angle formed between the terminal side of the given angle and the x-axis. It helps find exact trigonometric values by relating them to known angles in the first quadrant. For 4π/3, the reference angle is π/3, which simplifies finding sin(4π/3) using known sine values.
Recommended video:

Reference Angles on the Unit Circle
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
740
views


