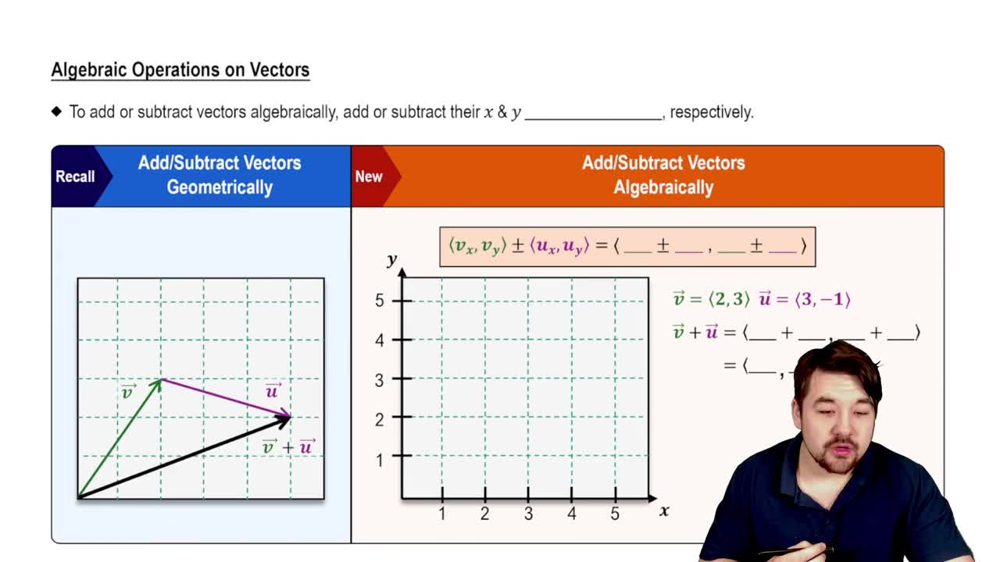
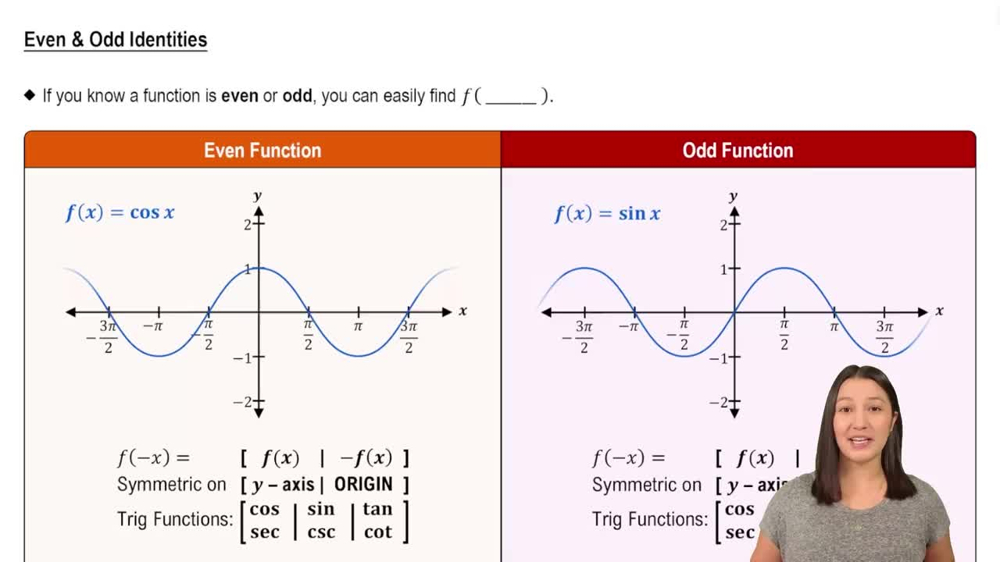
Textbook Question
Find the given distances between points P, Q, R, and S on a number line, with coordinates -4, -1, 8, and 12, respectively. See Example 3. d (P, Q)
460
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: