Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
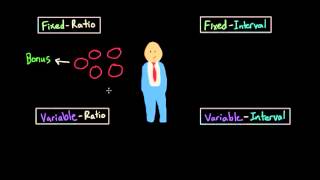
6. Learning
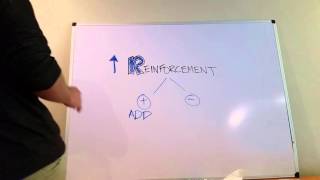
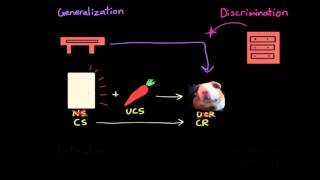
Classical Conditioning
Multiple Choice
Multiple ChoiceWhen a previously neutral stimulus, through repeated pairing with the unconditioned stimulus, begins to cause the same kind of reflexive response, the neutral stimulus has become
A
a reflex.
B
a discriminative stimulus.
C
extinct.
D
a conditioned stimulus.
Related Videos
Related Practice
















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)