Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
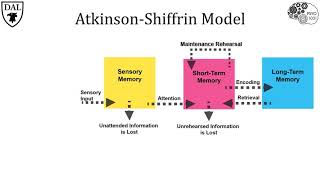
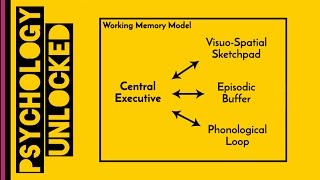
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Long-term memories may be inaccessible because
A
of interference.
B
most of them are actually lost.
C
most people do not try hard enough to retrieve them.
D
they were not paid attention to in the first place.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of long-term memory: Long-term memory refers to the storage of information over an extended period. It is a crucial part of our memory system, allowing us to retain knowledge and experiences.
Identify the potential reasons for inaccessibility of long-term memories: The problem provides several options, including interference, actual loss of memories, lack of effort in retrieval, and lack of initial attention.
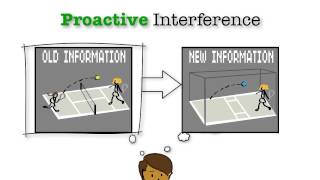
Explore the concept of interference: Interference occurs when other information in memory competes with or disrupts the retrieval of the desired memory. This can be proactive (old memories interfering with new ones) or retroactive (new memories interfering with old ones).
Consider the likelihood of memory loss: While some memories may fade over time, the idea that most long-term memories are lost is less supported by research compared to interference.
Evaluate the role of attention and retrieval effort: While attention is crucial for encoding memories, the problem focuses on inaccessibility, which is more related to retrieval issues like interference rather than initial attention or effort in retrieval.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)