Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
5. Consciousness and Sleep
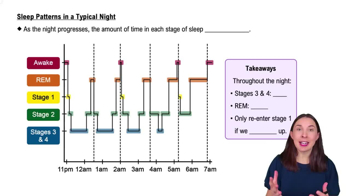
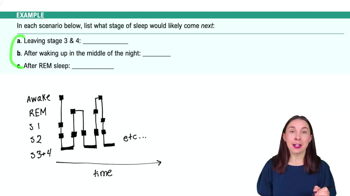
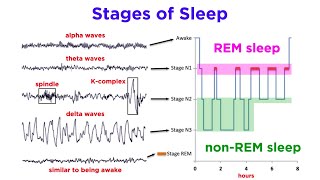
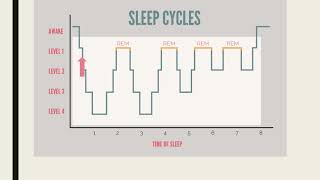
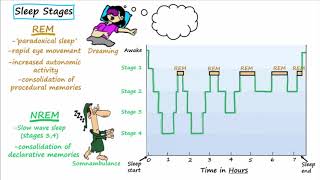
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Eventually, everyone must sleep due to our
A
need for mental rest.
B
delta waves.
C
beta waves.
D
biological rhythms.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of biological rhythms: Biological rhythms are natural cycles of change in our body's chemicals or functions. They are crucial for regulating sleep, wakefulness, and other bodily functions.
Recognize the role of sleep in biological rhythms: Sleep is a vital part of our biological rhythms, specifically the circadian rhythm, which is a 24-hour cycle that influences sleep-wake patterns.
Differentiate between different brain waves: Delta waves are associated with deep sleep, while beta waves are linked to active thinking and alertness. These waves are part of the sleep cycle but not the primary reason for the need to sleep.
Identify the necessity of sleep: Sleep is essential for mental and physical restoration, memory consolidation, and maintaining cognitive functions, all of which are regulated by biological rhythms.
Conclude that the need for sleep is driven by biological rhythms: Biological rhythms ensure that our body follows a regular pattern of sleep and wakefulness, highlighting their importance in the necessity of sleep.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)