Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
4. Sensation and Perception
Visual Anatomy
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
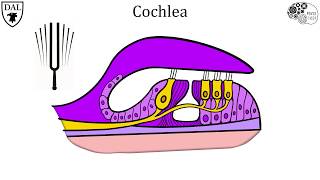
Normal aging causes loss of hair cells in the
A
eardrum.
B
pinna.
C
cochlea.
D
ear canal.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
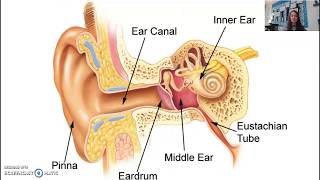
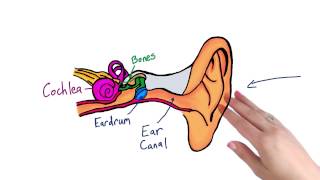
Understand the anatomy of the ear: The ear is composed of several parts including the outer ear (pinna and ear canal), the middle ear (eardrum), and the inner ear (cochlea).
Recognize the function of each part: The pinna collects sound waves, the ear canal directs them to the eardrum, the eardrum vibrates in response to sound, and the cochlea converts these vibrations into neural signals.
Identify the role of hair cells: Hair cells are sensory cells located in the cochlea. They play a crucial role in converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as sound.
Consider the effects of aging: Normal aging can lead to the degeneration of hair cells, particularly in the cochlea, which can result in hearing loss.
Conclude the specific location of hair cell loss: Given the role and location of hair cells, the cochlea is the part of the ear where hair cell loss due to aging typically occurs.

 3:08m
3:08mWatch next
Master Anatomy of the Eye with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















![The Human Eye & Color Blindness [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 3] (3.3)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Mwq23JTBnN0/mqdefault.jpg)







![The Process Of Smelling & Tasting [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 6] (3.6)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/vIQf0QAJFQA/mqdefault.jpg)




![Sensation of Touch, Layers of Skin & Pain [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 7] (3.7)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/sjbg9pf9Cj8/mqdefault.jpg)























![Factors affecting perception - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ot4AjaQUo3Y/mqdefault.jpg)
![Social & Cognitive Factors In Learning [AP Psychology Unit 4 Topic 4] (4.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Z1NIcVXplFk/mqdefault.jpg)