Table of contents
- 0. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra3h 29m
- 1. Equations and Inequalities3h 27m
- 2. Graphs1h 43m
- 3. Functions & Graphs2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 54m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Measuring Angles40m
- 8. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 9. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 10. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 11. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trig Equations1h 41m
- 12. Trigonometric Identities 2h 34m
- 13. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 14. Vectors2h 25m
- 15. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 16. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 17. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
- 18. Systems of Equations and Matrices3h 6m
- 19. Conic Sections2h 36m
- 20. Sequences, Series & Induction1h 15m
- 21. Combinatorics and Probability1h 45m
- 22. Limits & Continuity1h 49m
- 23. Intro to Derivatives & Area Under the Curve2h 9m
20. Sequences, Series & Induction
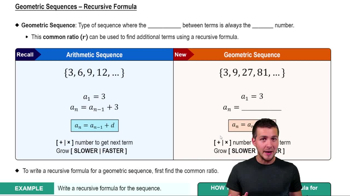
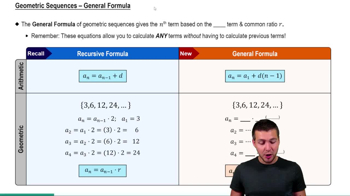
Geometric Sequences
Struggling with Precalculus?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Write a formula for the general or nth term of the geometric sequence where a7=1458 and r=−3.
A
an=1⋅(−3)n−1
B
an=2⋅(−3)n−1
C
an=−32⋅(−3)n−1
D
an=32⋅(−3)n−1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the formula for the nth term of a geometric sequence, which is given by: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mi>n</mi></sub><mo>=</mo><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub><mo>⋅</mo><msup><mi>r</mi><mrow><mi>n</mi><mo>-</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow></msup></math>, where <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub></math> is the first term and <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>r</mi></math> is the common ratio.
Use the given information that <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>7</mn></sub><mo>=</mo><mn>1458</mn></math> and <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>r</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>-</mo><mn>3</mn></math> to set up the equation for the 7th term: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mn>1458</mn><mo>=</mo><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub><mo>⋅</mo><msup><mo>(</mo><mo>-</mo><mn>3</mn><mo>)</mo><mn>6</mn></msup></math>.
Calculate <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><msup><mo>(</mo><mo>-</mo><mn>3</mn><mo>)</mo><mn>6</mn></msup></math> to find the value of the common ratio raised to the power of 6.
Solve for <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub></math> by dividing both sides of the equation by <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><msup><mo>(</mo><mo>-</mo><mn>3</mn><mo>)</mo><mn>6</mn></msup></math>.
Substitute the value of <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub></math> and <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>r</mi></math> into the nth term formula to write the general term: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><mi>a</mi><sub><mi>n</mi></sub><mo>=</mo><mi>a</mi><sub><mn>1</mn></sub><mo>⋅</mo><msup><mo>(</mo><mo>-</mo><mn>3</mn><mo>)</mo><mrow><mi>n</mi><mo>-</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow></msup></math>.

 4:18m
4:18mWatch next
Master Geometric Sequences - Recursive Formula with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice