Table of contents
- 0. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra3h 29m
- 1. Equations and Inequalities3h 27m
- 2. Graphs1h 43m
- 3. Functions & Graphs2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 54m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Measuring Angles40m
- 8. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 9. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 10. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 11. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trig Equations1h 41m
- 12. Trigonometric Identities 2h 34m
- 13. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 14. Vectors2h 25m
- 15. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 16. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 17. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
- 18. Systems of Equations and Matrices3h 6m
- 19. Conic Sections2h 36m
- 20. Sequences, Series & Induction1h 15m
- 21. Combinatorics and Probability1h 45m
- 22. Limits & Continuity1h 49m
- 23. Intro to Derivatives & Area Under the Curve2h 9m
18. Systems of Equations and Matrices
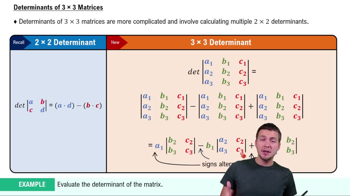
Determinants and Cramer's Rule
Struggling with Precalculus?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Write each equation in standard form and use Cramer's Rule to solve the system.
y=−3x+4
−2x=7y−9
A
x=1,y=1
B
x=−1,y=1
C
x=1,y=−1
D
x=−1,y=−1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
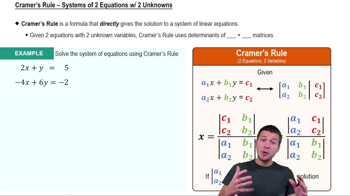
First, rewrite each equation in standard form, which is Ax + By = C. For the first equation y = -3x + 4, rearrange it to 3x + y = 4.
For the second equation -2x = 7y - 9, rearrange it to 2x + 7y = 9.
Now, you have the system of equations in standard form: 3x + y = 4 and 2x + 7y = 9.
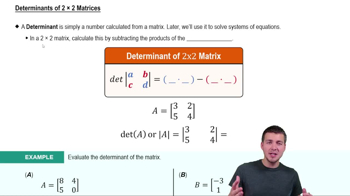
To use Cramer's Rule, calculate the determinant of the coefficient matrix, which is |A| = (3)(7) - (1)(2).
Next, calculate the determinants for x and y using the matrices formed by replacing the respective columns with the constants from the right-hand side of the equations, and solve for x and y using Cramer's Rule: x = Dx/|A| and y = Dy/|A|.

 4:36m
4:36mWatch next
Master Determinants of 2×2 Matrices with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning