Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Magnetic Flux
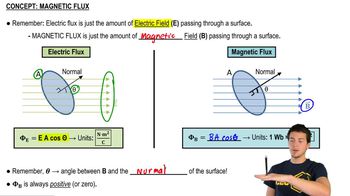
Magnetic flux is a measure of the quantity of magnetism, taking into account the strength and the extent of a magnetic field. It is calculated as the product of the magnetic field strength (B) and the area (A) through which the field lines pass, adjusted for the angle (θ) between the field lines and the normal to the surface. The formula is given by Φ = B * A * cos(θ). In this scenario, the angle changes as the coil rotates, affecting the flux.
Recommended video:
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday's Law states that a change in magnetic flux through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the circuit. The induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux. This principle is fundamental in understanding how the rotation of the coil in a magnetic field leads to changes in the magnetic flux, which can induce current in the coil.
Recommended video:
Area and Orientation of the Coil
The area of the coil and its orientation relative to the magnetic field are crucial in determining the magnetic flux. The area is a fixed value, but the orientation affects the angle θ in the magnetic flux formula. Initially, when the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the flux is maximized, while it becomes zero when parallel, illustrating how orientation directly influences the magnetic flux experienced by the coil.
Recommended video:
Calculating Work As Area Under F-x Graphs
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance