Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday's Law states that the electromotive force (emf) induced in a closed loop is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop. In this scenario, as the coil moves through the magnetic field, the area exposed to the field changes, leading to a change in magnetic flux and thus inducing an emf.
Recommended video:
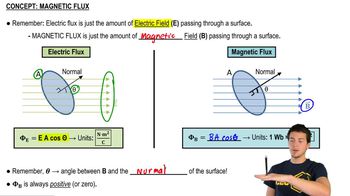
Magnetic Flux
Magnetic flux is defined as the product of the magnetic field strength (B) and the area (A) through which the field lines pass, taking into account the angle between the field and the normal to the surface. In this case, since the coil's plane is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the magnetic flux is maximized, which is crucial for calculating the induced emf.
Recommended video:
Induced EMF and Speed Relationship
The induced emf in a coil moving through a magnetic field is influenced by the speed of the coil. According to Faraday's Law, if the speed (v) of the coil is increased, the rate at which the magnetic flux changes also increases, leading to a higher induced emf. Therefore, tripling both the speed and the magnetic field will result in a tripling of the induced emf.
Recommended video: