Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Kirchhoff's Loop Rule
Kirchhoff's Loop Rule states that the sum of the potential differences (voltage) around any closed loop in a circuit must equal zero. This principle is based on the conservation of energy, indicating that the energy supplied by the sources (like batteries) is equal to the energy consumed by the resistors in the loop.
Recommended video:
Intro to Kirchhoff's Loop Rule
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit, expressed as V = IR. This fundamental relationship allows us to calculate the voltage across a resistor when the current flowing through it and its resistance are known, which is essential for analyzing circuits.
Recommended video:
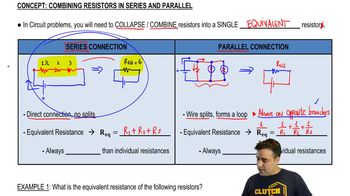
Series and Parallel Resistors
In circuits, resistors can be arranged in series or parallel configurations. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance can be found using the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... This distinction is crucial for calculating the overall resistance and current in the circuit.
Recommended video:
Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel